VEGFA (Isoform 189) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: 339/H2]
CAT#: AM33406BT-N
VEGFA (Isoform 189) mouse monoclonal antibody, clone 339/H2, Biotin, Purified
Conjugation: Unconjugated
Need it in bulk or conjugated?
Get a free quote
CNY 4,367.00
货期*
5周
规格
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Clone Name | 339/H2 |
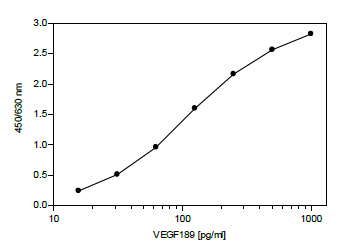
| Applications | ELISA |
| Recommend Dilution | ELISA: 1-5 µg/ml. |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Recombinant Human VEGF189 protein (45 kDa) derived from E.coli (Cat.-No AR31182PU). |
| Specificity | In Western Blot, this unconjugated antibody recognizes the unreduced and reduced protein. There is a weak cross reactivity with Mouse VEGF-A visible. |
| Formulation | PBS Label: Biotin State: Purified State: Lyophilized purified IgG fraction purified from Cell Culture Supernatant Stabilizer: 50x BSA Preservative: 0.02% Sodium Azide |
| Reconstitution Method | Restore in sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/ml. Centrifuge vial prior to opening. |
| Purification | Protein G Chromatography |
| Conjugation | Biotin |
| Storage Condition | Store lyophilized at 2-8°C for 6 months or at -20°C long term. After reconstitution store the antibody undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C long term. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Gene Name | vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| Database Link | |
| Background | Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF or VEGF-A), also known as vascular permeability factor (VPF) or vasculotropin, is a homodimeric 34 - 42 kDa, heparin-binding glycoprotein with potent angiogenic, mitogenic and vascular permeability-enhancing activities specific for endothelial cells. Different isoforms can be generated by differential splicing (e.g. VEGF165). All eight cysteine residues involved in intra- and inter-chain disulfide bonds are conserved among these growth factors. A cDNA encoding a protein having a 53% amino acid sequence homology in the PDGF-like region of VEGF has been isolated from a human placental cDNA library. This protein, named placenta growth factor (PlGF), is now recognized to be a member of the VEGF family of growth factors. Two receptor tyrosine kinases have been described as putative VEGF receptors. Flt-1 (fms-like tyrosine kinase), and KDR (kinase-insert-domain-containing receptor) proteins have been shown to bind VEGF-A with high affinity. In vitro, VEGF is a potent endothelial cell mitogen. In cultured endothelial cells, VEGF can activate phospholipase C and induce rapid increases of free cytosolic Ca2+. VEGF has also been shown to be chemotactic for monocytes and osteoblasts. In vivo, VEGF can induce angiogenesis as well as increase microvascular permeability. As a vascular permeability factor, VEGF acts directly on the endothelium and does not degranulate mast cells. Based on its in vitro and in vivo properties, VEGF is expected to play important roles in inflammation and during normal and pathological angiogenesis, a process that is associated with wound healing, embryonic development, and growth and metastasis of solid tumors. |
| Synonyms | VEGFA, VEGF, VPF, Vascular endothelial growth factor A, Vascular permeability factor |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
| 抗体相关资料 |
Customer
Reviews
Loading...


 United States
United States
 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China