GFAP (NM_002055) Human Recombinant Protein
CAT#: TP304548L
Recombinant protein of human glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), transcript variant 1, 1 mg
|
Need it in bulk or customized? Get a free quote |
Avi-tag Biotinylated Protein Get a free quote |
CNY 36,000.00
CNY 1,999.00
CNY 2,700.00
CNY 600.00
CNY 1,050.00
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | HEK293T |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
>RC204548 protein sequence
Red=Cloning site Green=Tags(s) MERRRITSAARRSYVSSGEMMVGGLAPGRRLGPGTRLSLARMPPPLPTRVDFSLAGALNAGFKETRASER AEMMELNDRFASYIEKVRFLEQQNKALAAELNQLRAKEPTKLADVYQAELRELRLRLDQLTANSARLEVE RDNLAQDLATVRQKLQDETNLRLEAENNLAAYRQEADEATLARLDLERKIESLEEEIRFLRKIHEEEVRE LQEQLARQQVHVELDVAKPDLTAALKEIRTQYEAMASSNMHEAEEWYRSKFADLTDAAARNAELLRQAKH EANDYRRQLQSLTCDLESLRGTNESLERQMREQEERHVREAASYQEALARLEEEGQSLKDEMARHLQEYQ DLLNVKLALDIEIATYRKLLEGEENRITIPVQTFSNLQIRETSLDTKSVSEGHLKRNIVVKTVEMRDGEV IKESKQEHKDVM TRTRPLEQKLISEEDLAANDILDYKDDDDKV |
| Tag | C-Myc/DDK |
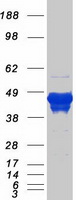
| Predicted MW | 49.7 kDa |
| Concentration | >0.1 µg/µL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Purity | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Buffer | 25 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM glycine, pH 7.3, 10% glycerol |
| Preparation | Recombinant protein was captured through anti-DDK affinity column followed by conventional chromatography steps. |
| Note | For testing in cell culture applications, please filter before use. Note that you may experience some loss of protein during the filtration process. |
| Storage | Store at -80°C. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from the date of receipt of the product under proper storage and handling conditions. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Bioactivity | WB positive control (PMID: 29774780) |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_002046 |
| Locus ID | 2670 |
| UniProt ID | P14136 |
| Refseq Size | 3097 |
| Cytogenetics | 17q21.31 |
| Refseq ORF | 1296 |
| Synonyms | ALXDRD |
| Summary | This gene encodes one of the major intermediate filament proteins of mature astrocytes. It is used as a marker to distinguish astrocytes from other glial cells during development. Mutations in this gene cause Alexander disease, a rare disorder of astrocytes in the central nervous system. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008] |
| Protein Families | ES Cell Differentiation/IPS |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |


 United States
United States
 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China