Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer found in women globally, and it's primarily caused by persistent high-risk HPV infection. Cervical cancer, which develops in the tissues of the cervix, can be classified into two types: squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Several studies have led to the discovery of a range of biomarkers, including several polymorphisms, microRNAs, mRNA, and serum biomarkers. OriGene offers antibodies, plasmids, and recombinant proteins for the most prominent cervical cancer biomarkers.
Explore All Cervical Cancer Products
Potential biomarkers 1, 2, 3, 4
HPV E6-E7 ANXA2 ASF1B A1AT PYCR2 TTR ApoA-1 VDBPKey genes mutated in cervical cancer 5
CASP8 ERBB3 HLA-A MED1 SHKBP1 TGFBR2Other genes
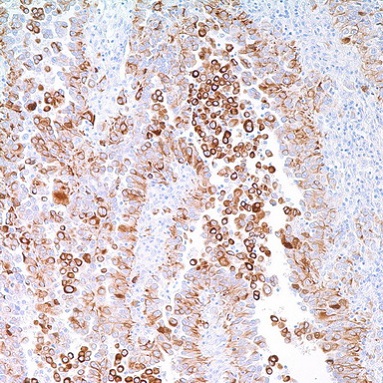
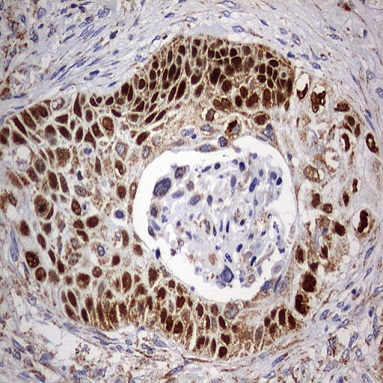
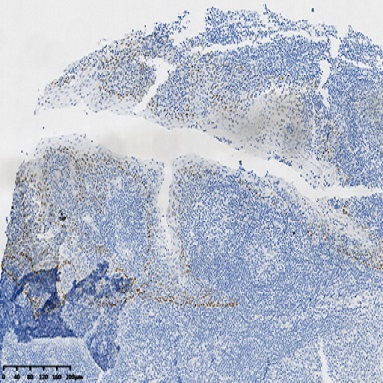
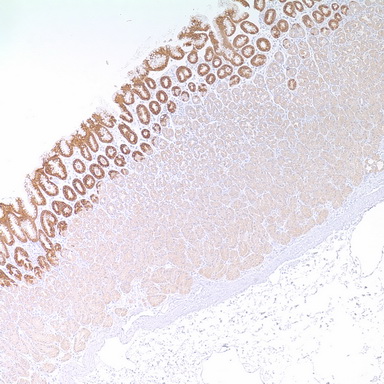
PD-L1 PD-L2 KRAS ARID1A PTENOne of the challenges in cervical cancer is to distinguish between squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) from adenocarcinoma (AEC) 6 In a recent study, Li et al. showed that a combination of cytokeratin 5/6 (CK5/6), p63, p40 and MUC5AC are useful in differentiating cervical adenocarcinoma from cervical squamous cell carcinoma using immunohistochemistry 7
Products for Cervical Cancer Research
References:
- Pal A, Kundu R. Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7: The Cervical Cancer Hallmarks and Targets for Therapy. Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 21;10:3116.
- Wang Z, Jiang C, Pang L, Jia W, Wang C, Gao X, Zhang X, Dang H, Ren Y. ANXA2 is a potential marker for the diagnosis of human cervical cancer. Biomark Med. 2021 Jan;15(1):57-67.
- Liu X, Song J, Zhang Y, Wang H, Sun H, Feng X, Hou M, Chen G, Tang Q, Ji M. ASF1B promotes cervical cancer progression through stabilization of CDK9. Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 26;11(8):705
- Keeratichamroen S, Subhasitanont P, Chokchaichamnankit D, Weeraphan C, Saharat K, Sritana N, Kantathavorn N, Wiriyaukaradecha K, Sricharunrat T, Paricharttanakul NM, Auewarakul C, Svasti J, Srisomsap C. Identification of potential cervical cancer serum biomarkers in Thai patients. Oncol Lett. 2020 Jun;19(6):3815-3826.
- Burk R. et al. The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network., Nature 543, 378–384 (2017).
- Li H, Jing X, Yu J, et al. A combination of cytokeratin 5/6, p63, p40 and MUC5AC are useful for distinguishing squamous cell carcinoma from adenocarcinoma of the cervix. Diagn Pathol. 2020;15(1):104
- Ma Y et al. Expression of p63 and CK5/6 in early-stage lung squamous cell carcinoma is not only an early diagnostic indicator but also correlates with a good prognosis. Thorac Cancer. 2015;6(3):288–95.


 United States
United States
 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China